The purpose of the study is to examine and try to understand, in some way, if Wenger’s Community of Practice (CoP) framework makes a difference within the research or experiential lives of those who conduct autoethnographic research, especially given that many in the larger research community still see this as a contested strategy of inquiry.
While there are numerous works from Wenger that I will detail in my literature section, the two that I have in mind at this point is his
Wenger, E. (1999). Learning as social participation. Knowledge Management Review, 1(6), 30-33.
Wenger, E. (n.d.). Communities of practice: A brief introduction. Retrieved from http://www.ewenger.com/theory/communities_of_practice_intro.htm
I am being guided by Wenger’s Model (from the first article):
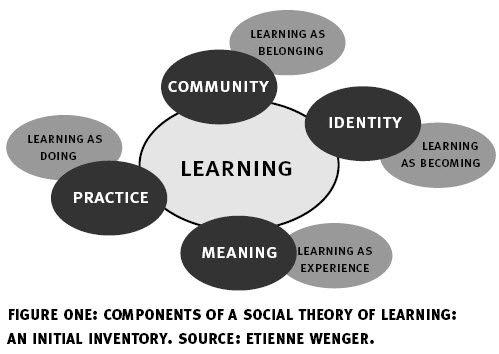
and from his defininition (from the second reference above):
Communities of practice are groups of people who share a concern or a passion for something they do and learn how to do it better as they interact regularly.
where he discusses them as (also from the second reference above):
Note that this definition allows for, but does not assume, intentionality: learning can be the reason the community comes together or an incidental outcome of member’s interactions. Not everything called a community is a community of practice. A neighborhood for instance, is often called a community, but is usually not a community of practice. Three characteristics are crucial:
1. The domain: A community of practice is not merely a club of friends or a network of connections between people. It has an identity defined by a shared domain of interest. Membership therefore implies a commitment to the domain, and therefore a shared competence that distinguishes members from other people. (You could belong to the same network as someone and never know it.) The domain is not necessarily something recognized as “expertise” outside the community. A youth gang may have developed all sorts of ways of dealing with their domain: surviving on the street and maintaining some kind of identity they can live with. They value their collective competence and learn from each other, even though few people outside the group may value or even recognize their expertise.
2. The community: In pursuing their interest in their domain, members engage in joint activities and discussions, help each other, and share information. They build relationships that enable them to learn from each other. A website in itself is not a community of practice. Having the same job or the same title does not make for a community of practice unless members interact and learn together. The claims processors in a large insurance company or students in American high schools may have much in common, yet unless they interact and learn together, they do not form a community of practice. But members of a community of practice do not necessarily work together on a daily basis. The Impressionists, for instance, used to meet in cafes and studios to discuss the style of painting they were inventing together. These interactions were essential to making them a community of practice even though they often painted alone.
3. The practice: A community of practice is not merely a community of interest–people who like certain kinds of movies, for instance. Members of a community of practice are practitioners. They develop a shared repertoire of resources: experiences, stories, tools, ways of addressing recurring problems�in short a shared practice. This takes time and sustained interaction. A good conversation with a stranger on an airplane may give you all sorts of interesting insights, but it does not in itself make for a community of practice. The development of a shared practice may be more or less self-conscious. The “windshield wipers” engineers at an auto manufacturer make a concerted effort to collect and document the tricks and lessons they have learned into a knowledge base. By contrast, nurses who meet regularly for lunch in a hospital cafeteria may not realize that their lunch discussions are one of their main sources of knowledge about how to care for patients. Still, in the course of all these conversations, they have developed a set of stories and cases that have become a shared repertoire for their practice.
The interview discussion will be informal and topics may emerge as ideas are exchanged. I hope to address (2) areas of inquiry:
1. What support or encouragement do you (or did you) have when you engage(d) in your research?
2. Do you find yourself a member of any identifiable community (of practice) that plays a role with your autoethnographic research?